Large Magnetic Particle Brake - Rated up to 425W Heat Dissipation & 1800 RPM Speed
Large Magnetic Particle Brake - Rated up to 425W Heat Dissipation & 1800 RPM Speed
SKU:LAR-57697d
Precision torque control with 425W Heat Dissipation & 1800 RPM Speed for reliable performance in tension control & load simulation.
Regular price
$1,299.99
Regular price
Sale price
$1,299.99
Unit price
per
Delivery via Maden
Expect your order to arrive on time.
Secure Payments
All orders are processed through a secure, PCI-compliant checkout.

The Large Magnetic Particle Brake, with a torque range of 0.5 to 38 lb-ft, offers precise torque control ideal for tension control, load simulation, and soft stops. With slip heat dissipation of 190 to 425 W and a maximum speed of 1800 RPM, this self-contained brake ensures smooth and repeatable performance, independent of shaft speed. Designed with a configuration of shaft on one side, it is reliable for applications requiring adjustable tension and torque limiting. The brake also features a shaft that couples to the case with electrical excitation, offering efficient control over load torque.
Product Specifications
Characteristics Characteristics
With no electrical excitation, the shaft freely rotates.With electrical excitation, the shaft becomes coupled to the case.While the load torque is less than the output torque, the shaft wonât rotate.When the load torque is increased, the brake will slip smoothly at the torque level set by the coil input current.
Determining Proper Brake Size Determining Proper Brake Size
Determining Proper Brake SizeThe proper sized brake mustâ¦Have sufficient torqueBe able to dissipate the heatNo run above rated speedTorqueFor load simulation, torque limiting and similar applications, torque is already known.For web handling, torque must be calculated. First determine the desired tension in your web (wire, fabric, film etc.).Calculate Torque: Torque (lb-inches) = Tension (lbs) x Roll Diameter (inches) x 0.5Use the Full Roll Diameter for calculating the maximum torque needed. For applications with the web running over a pulley or between nip rollers (pinch rollers), use the pulley diameter as the roll diameter in the formula above. Always be conservative - select the next larger model if the application requires nearly the rated torqueRPM (must be less than the maximum allowable)For load simulation, torque limiting and similar applications, RPM is already known.For web handling, usually linear speed (Web Speed) is known, and RPM must be calculated.Calculate RPM: RPM = 3.8 x WEB SPEED (feet per minute)/ROLL DIAMETER (inches)Use the Full Roll Diameter to determine the slowest speed. Use the Core Diameter (empty spool diameter), to determine the fastest speed. For applications with the web running over a pulley or between nip rollers (pinch rollers), use the pulley diameter as the roll diameter.Slip Heat Dissipation (model must be physically large enough not to overheat)For any application.Calculate Heat Input: HEAT (watts) = TORQUE (lb-inches) x RPM x 0.012For unwinding applications.Calculate Heat Input: HEAT (watts) = WEB TENSION (lbs) x WEB SPEED (feet/minute)/44Duty CycleThe average heat input must be below the brake's heat dissipation rating. If the motion is intermittent, use the average speed for thermal (SLIP) calculations.
Note Note
Mounting holes - Standard: Imperial (inch), Optional: Metric
Specifications Available Direct Current Dc Coil Voltage
24 V
Specifications Configuration
Shaft on one side
Specifications Current
2.4 A
Specifications Maximum Overhung
125 lb | 550 N
Specifications Maximum Speed
1800 rpm
Specifications Resistance
8.2 Ω
Specifications Slip Heat Dissipation
190 to 425 W
Specifications Torque Range
0.5 to 38 lb·ft | 0.70 to 50 N·cm
Specifications Weight
31 lb | 14 kg
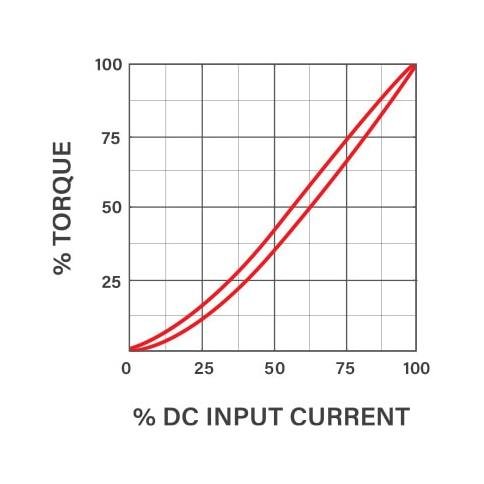
Torque Torque
Is proportional to input current.Is independent of RPM.
Applications Applications
Adjustable tension - for unwinding (payout) webs.Load simulation - for testing stepper motors, gear motors and mechanisms.Torque limitingSoft stops.


