Small Magnetic Particle Clutch - 2-56 N·cm Torque Range
Small Magnetic Particle Clutch - 2-56 N·cm Torque Range
SKU:SMA-8d7e99
Precise and repeatable torque control from 2 to 56 N·cm for various applications. Ideal for tension control, load simulation, and soft starts.
Regular price
$299.99
Regular price
Sale price
$299.99
Unit price
per
Delivery via Maden
Expect your order to arrive on time.
Secure Payments
All orders are processed through a secure, PCI-compliant checkout.
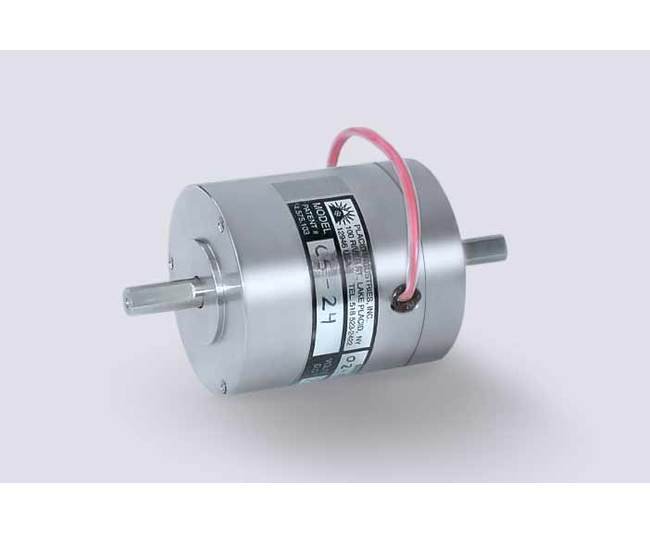

The Small Magnetic Particle Clutch with a torque range of 2 to 56 N·cm (up to 130 lb.-in./15 Nm) by Placid Industries offers precise and repeatable torque control suitable for various applications. Ideal for tension control, load simulation, torque limiting, and soft starts, this clutch ensures smooth operation independent of speed. With features like no electrical excitation for free rotation and linear torque vs. current characteristics, it meets the demands of institutional buyers requiring reliable performance.
Product Specifications
Characteristics Characteristics
With no electrical excitation, the input shaft & output shaft freely rotate.With electrical excitation, the output shaft becomes coupled to the input shaft.While the load torque is less than the output torque, the clutch drives without slip.When the load torque is increased, the clutch will slip smoothly at the torque level set by the coil input current.
Determining Proper Clutch Size Determining Proper Clutch Size
Determining Proper Clutch SizeThe proper sized clutch mustâ¦Have sufficient torqueBe able to dissipate the heatNo run above rated speedTorqueFor load simulation, torque limiting and similar applications, torque is already known.For web handling, torque must be calculated. First determine the desired tension in your web (wire, fabric, film etc.).Calculate Torque: Torque (lb-inches) = Tension (lbs) x Roll Diameter (inches) x 0.5Use the Full Roll Diameter for calculating the maximum torque needed. For applications with the web running over a pulley or between nip rollers (pinch rollers), use the pulley diameter as the roll diameter in the formula above. Always be conservative - select the next larger model if the application requires nearly the rated torqueRPM (must be less than the maximum allowable)For load simulation, torque limiting and similar applications, RPM is already known.For web handling, usually linear speed (Web Speed) is known, and RPM must be calculated.Calculate RPM: RPM = 3.8 x WEB SPEED (feet per minute)/ROLL DIAMETER (inches)Use the Full Roll Diameter to determine the slowest speed. Use the Core Diameter (empty spool diameter), to determine the fastest speed. For applications with the web running over a pulley or between nip rollers (pinch rollers), use the pulley diameter as the roll diameter.Slip Heat Dissipation (model must be physically large enough not to overheat)For any application.Calculate Heat Input: HEAT (watts) = TORQUE (lb-inches) x RPM x 0.012For unwinding applications.Calculate Heat Input: HEAT (watts) = WEB TENSION (lbs) x WEB SPEED (feet/minute)/44To minimize heat input in clutch applications, clutch input RPM should only be about 30-40 RPM faster than the fastest required output RPM. Faster slip speeds generate higher heat and wear with no benefit. Select a gearmotor ratio to achieve this.For applications with a large percentage change in roll diameter, use an automatic system to control the gearmotor, so the clutch input shaft is always 30 RPM faster than the output shaft. Mount a sensor on each clutch shaft to measure RPM. Connect to the controller. Program to maintain 30 RPM slip. The controller's 0-10v or 4-20mA output can control a variable speed motor drive. Select a varible speed drive to suit your motor.Duty CycleThe average heat input must be below the brake's heat dissipation rating. If the motion is intermittent, use the average speed for thermal (SLIP) calculations.
How Magnetic Particle Clutches Work How Magnetic Particle Clutch
The output disk/shaft does not touch the rotor. The gap in between is filled with a fine, dry stainless steel powder.The powder is free flowing, until a magnetic field is applied from the stationary coil. The powder particles form chains along the magnetic field lines, linking the disk to the rotor.The torque transmitted from input shaft to the output shaft is proportional to the magnetic field strength, and therefore to the applied D.C. input current.
Specifications Maximum Overhung
20 lb | 90 N
Specifications Maximum Speed
2000 rpm
Specifications Slip Heat Dissipation
10 W
Specifications Torque Range
3 to 80 oz·in | 2 to 56 N·cm
Specifications Weight
3 lb | 1.4 kg
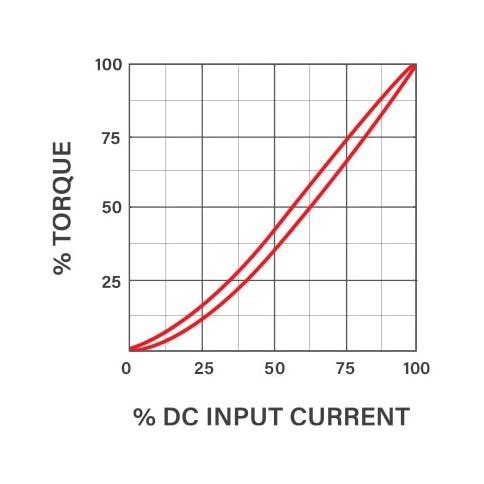
Torque Torque
Is proportional to input current.Is independent of RPM.
Applications Applications
Adjustable tension for rewinding websLoad simulationTorque limitingSoft starts


